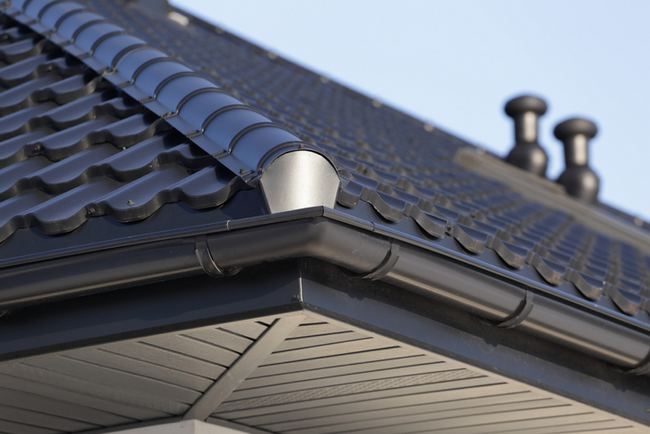
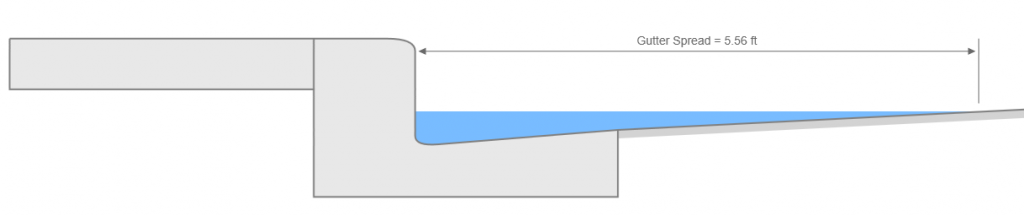
How To Determine Gutter Spread

Step 2 draw a line between the s and sxscales and note where it intersects the turning line.
How to determine gutter spread. N manning s coefficient. D flow depth at curb. How do you calculate gutter size. S x roadway cross slope.
You can measure pitch with a 2 foot level and a tape measure. From this depth and cross section geometry the gutter spread is computed. Once you know the total square footage of drainage for each gutter you ll need to adjust for the following two factors. The following procedure is used to design curb inlets on grade.
S longitudinal gutter slope. Determine the ratio of the width of flow in the depressed section w to the width of total gutter flow t using. That will show how much water a gutter will have to drain. Measure from the chalk mark to the opposite corner of the gutter making another chalk mark and moving the ladder again if necessary.
Divide the inch per hour watershed of the roof by the 5 minute rainfall intensity. T flow width. Ask gutter suppliers what size gutters will be needed to handle that amount. Carefully climb down the ladder and move it to the chalk mark.
Adjusting for pitch and rainfall. That is how much rain a roof can drain during the most intense rainfall. Find spread t given gutter flow q. If your gutter style and measurement matches one of the images click the corresponding button above to view more information and place your order scroll down to see additional gutter styles.
Compare calculated spread to the allowable spread. If you still do not see your gutter style then order sizing samples 3 sizes per box to determine which size gutterbrush best fits your gutter. E 0 ratio of depression flow to. Make a mark with chalk and record the measurement.
Kc 0 56 0 376 for compound cross slopes a trial and error procedure is used to compute d in the gutter sw and sx sections separately. The steeper a roof s pitch the more windblown rain it can collect. If relocating an intake recalculate q for the new drainage area s and calculate new values of spread. Compute depth of flow and ponded width t in the gutter section at the inlet.
If spread exceeds allowable limits relocate or resize the intake or add an additional intake. Step 1 determine input parameters including longitudinal slope s cross slope sx gutter flow q and manning s n. Q flow in gutter in cfs cms z reciprocal of the cross slope.