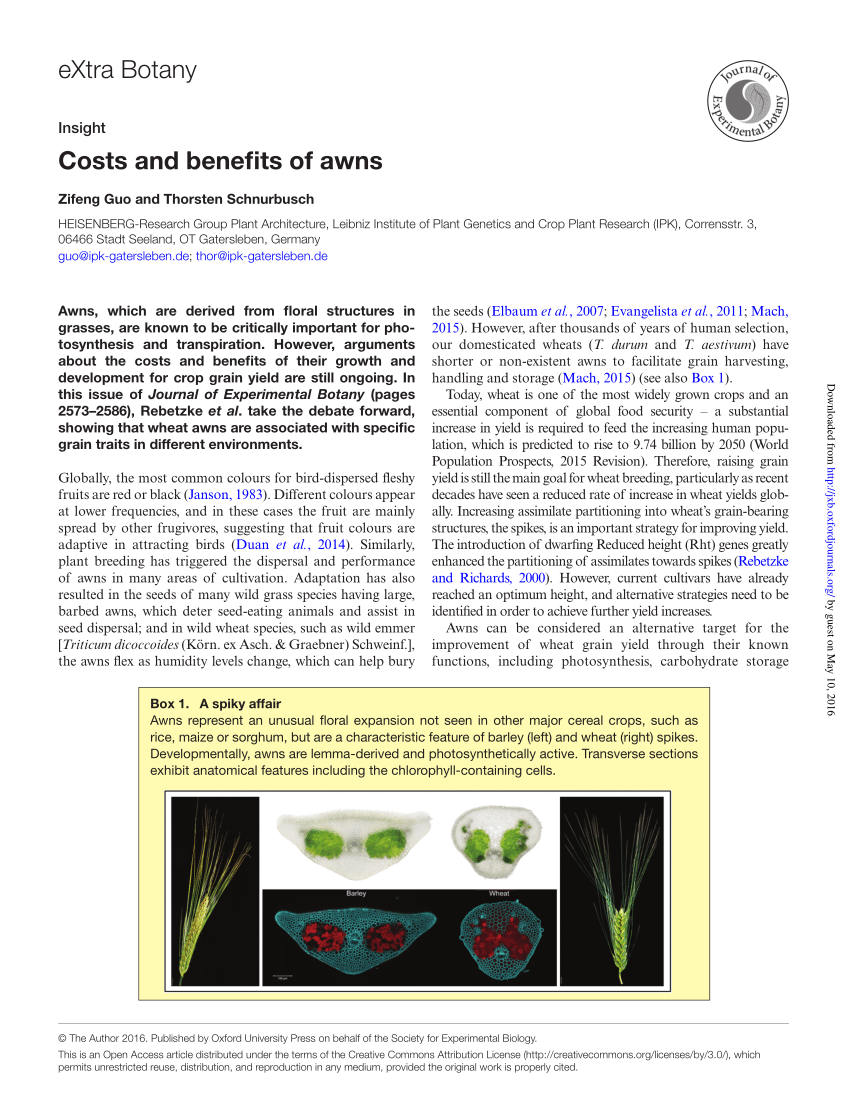
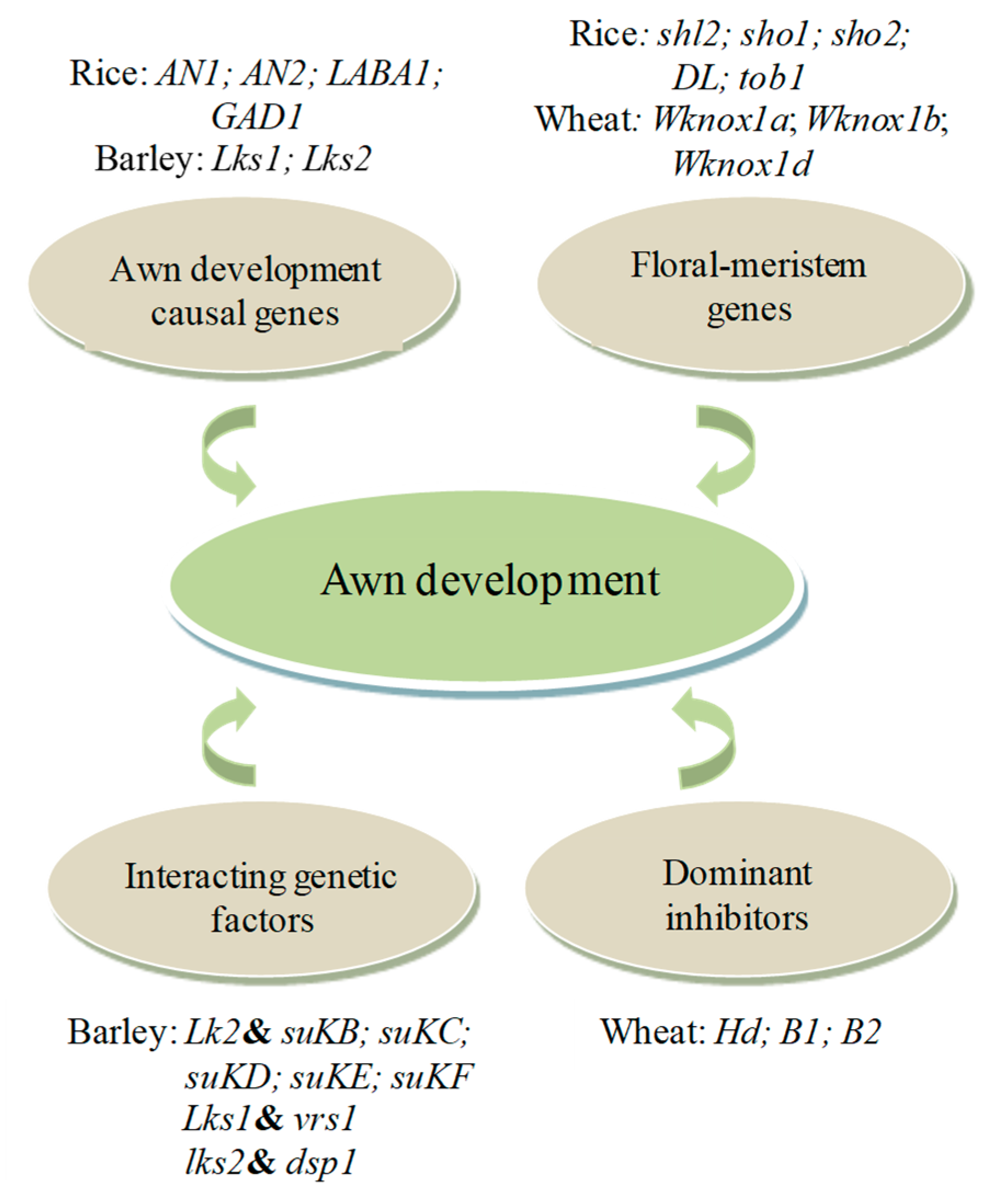
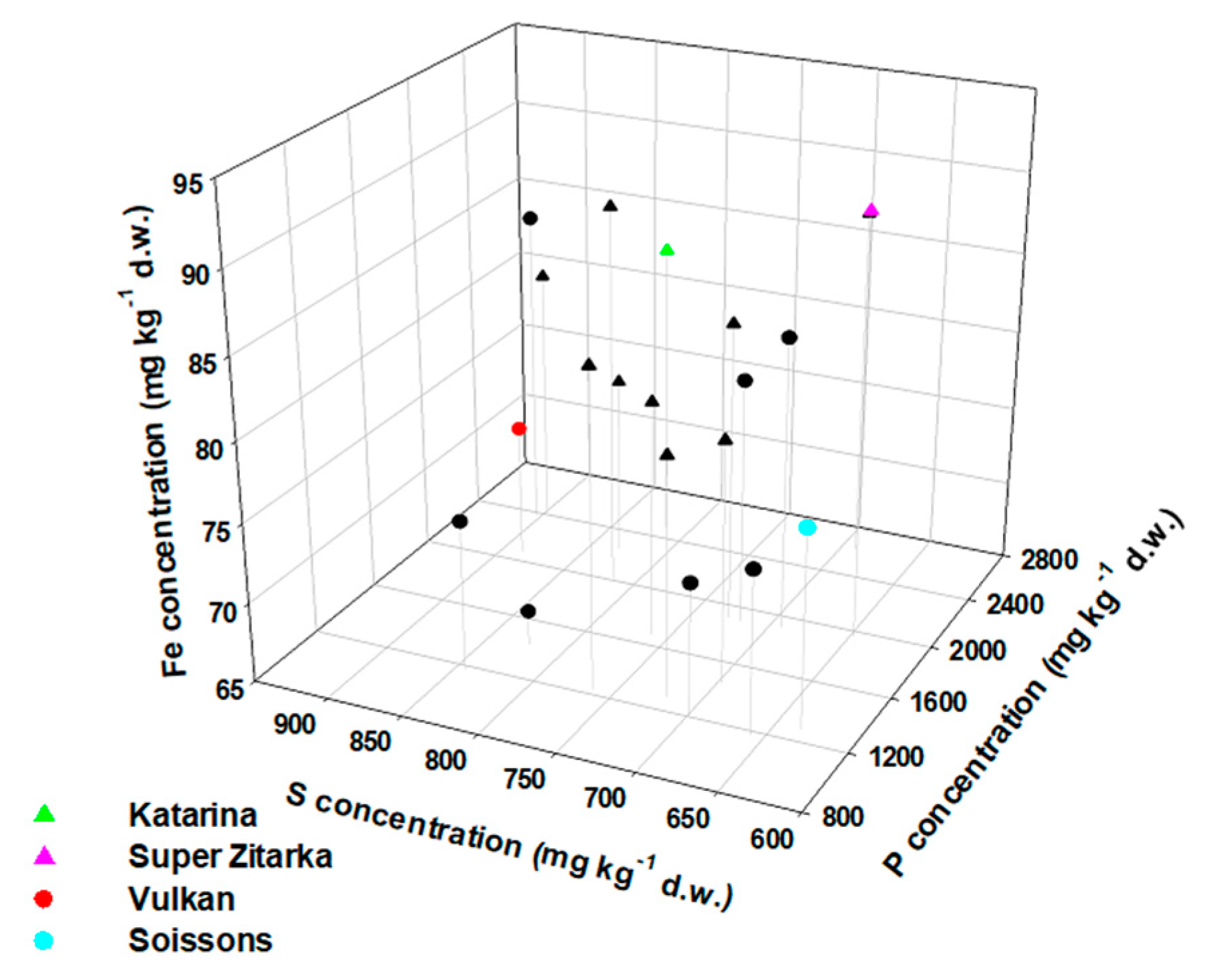
Importance Of Awns In Wheat

Abstract awn of wheat is an important photosynthetic and transpiration organ on spike.
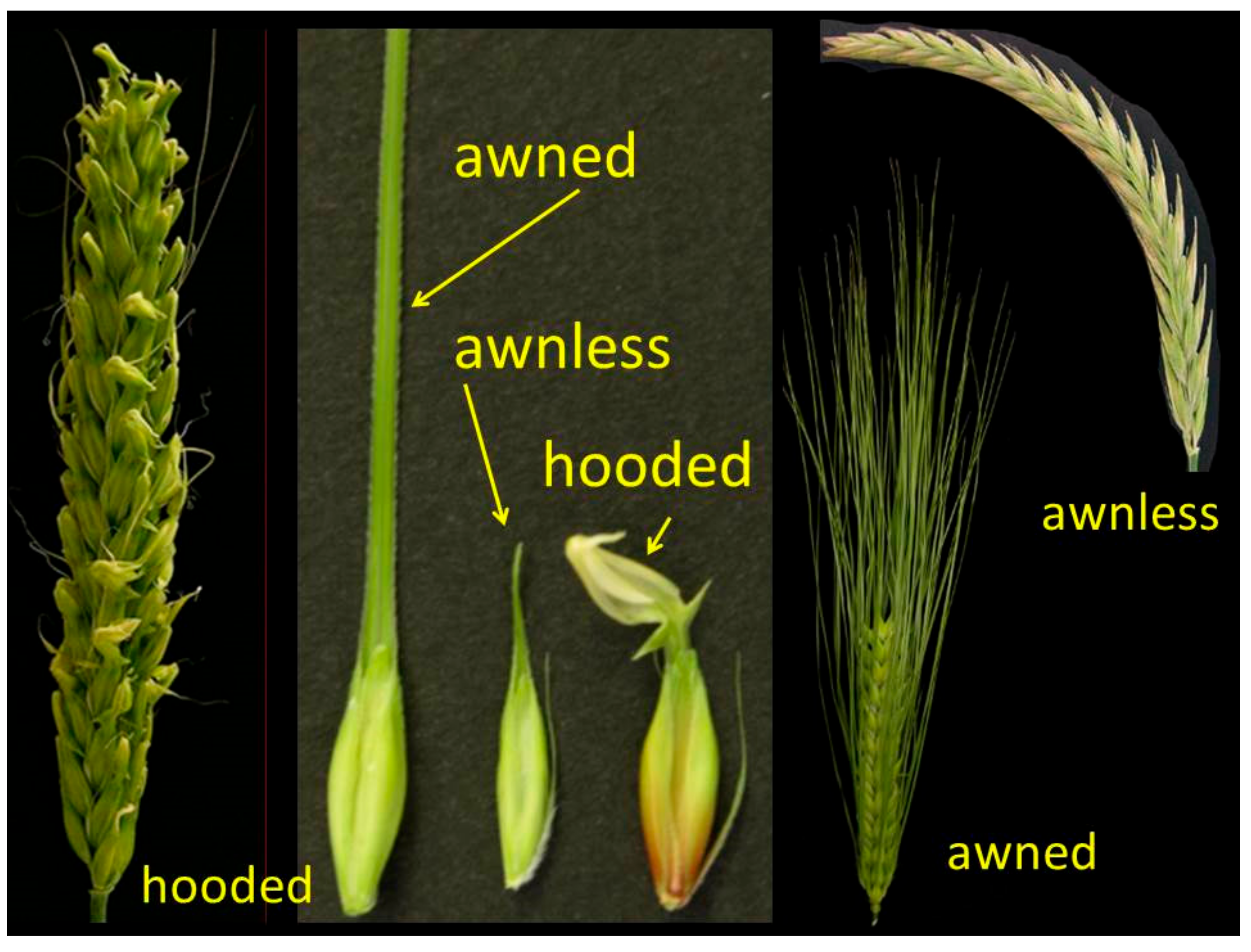
Importance of awns in wheat. Silicified hairs that cover th. In this study we identified two f 8 recombinant inbred lines rils that were segregating for awn length. Free threshing grain is another important domestication trait and is controlled by at least two groups of genes in wheat the tenacious glumes tg genes and the q locus on chromosome 5a. However the molecular mechanism underlying awnlessness remained unknown until recently.
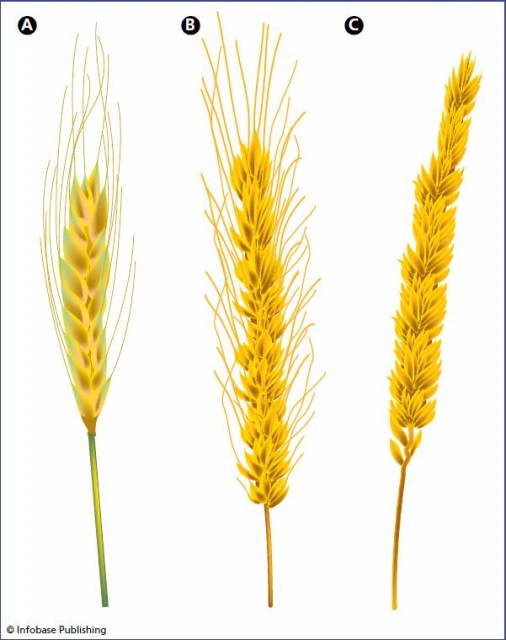
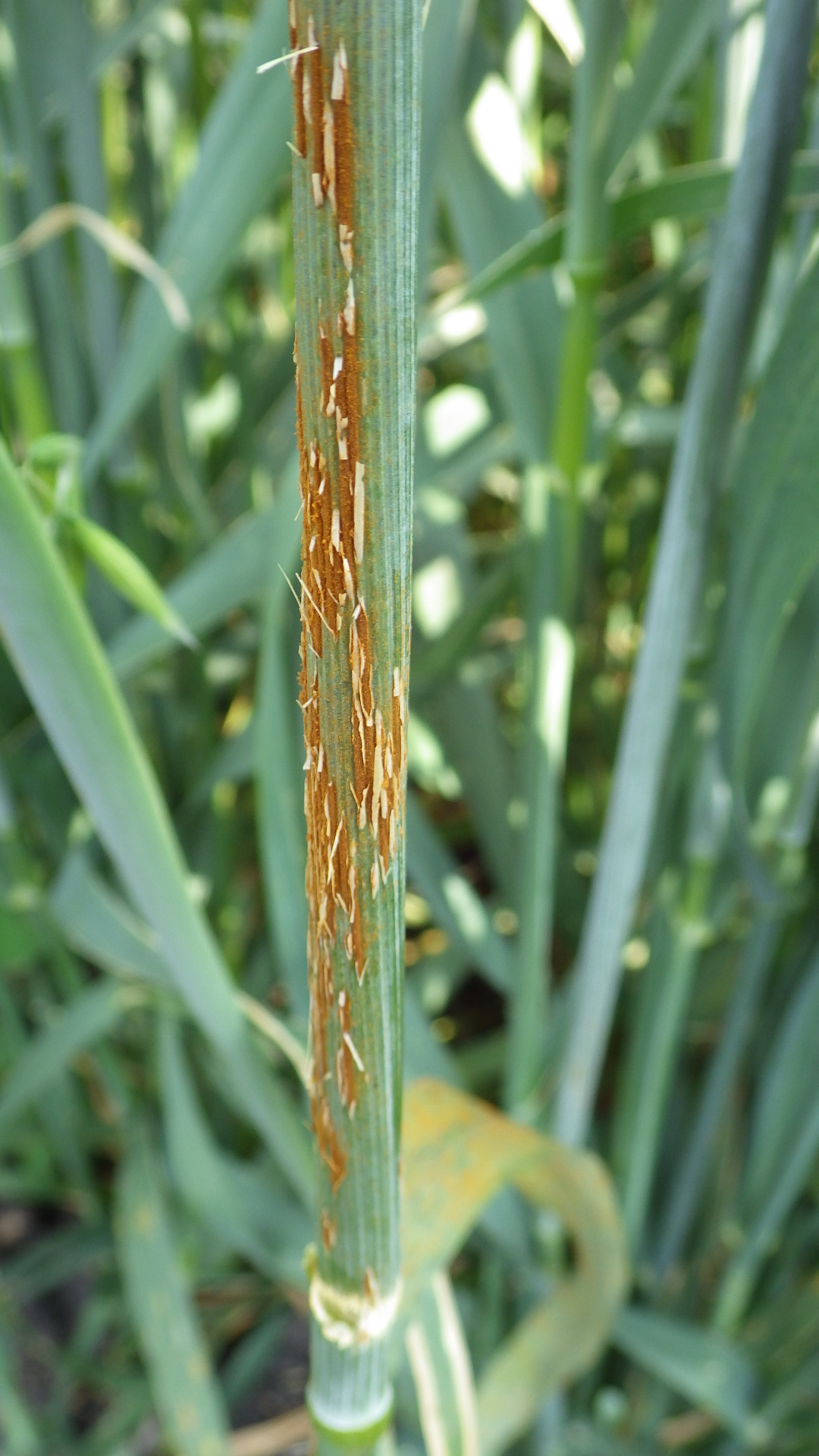
Awned wheat can survive in water deficient regions whose slender awns surrounding the wheatears are a hierarchical system possessing strong ability of capturing droplets from the mist environment for life maintenance. By craig harper. Three major awn inhibitors hd b1 and b2 are reported in wheat. Deer prefer awnless wheat.
The awns of wild emmer wheat spikelets effectively self cultivate by propelling themselves mechanically into soils. Healthy green growing wheat contains more than 20 percent crude protein and with less than 25 percent acid detergent fiber it is highly digestible. In order to identify the causal gene for awn length in the heterozygous inbred families hifs snps were called from rna sequencing rna seq data for hif. Winter wheat is an excellent cool season forage for white tailed deer.
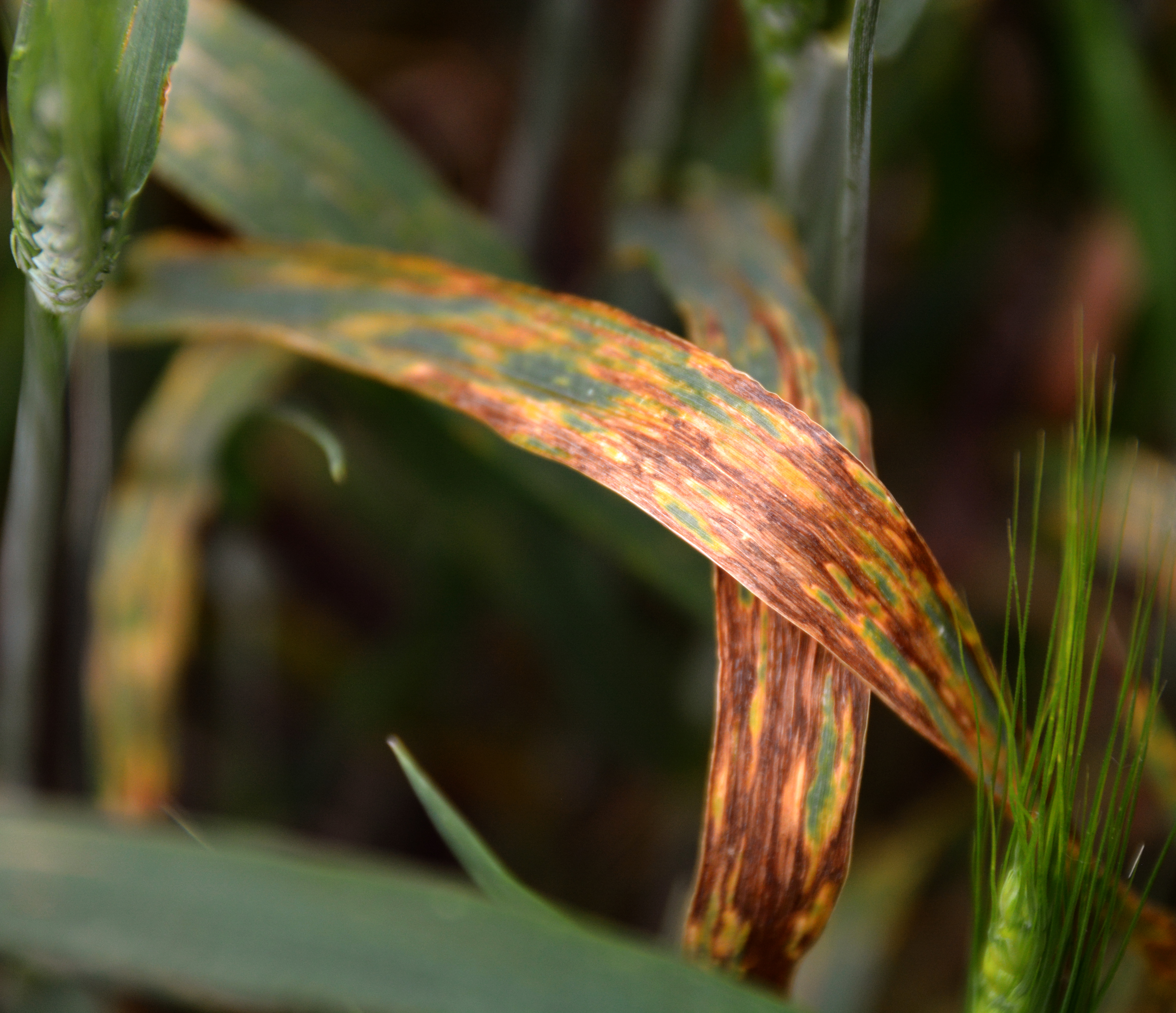
Awns play an important role in seed dispersal and photosynthesis of spikes. We discovered that the awns are also able to propel the seeds on and into the ground. Greater wue thermo tolerance and intrinsically higher photosynthetic potential of awns should translate to significantly greater yield potential for awned wheat varieties. In this study awn transverse sections of triticum monococcum triticum dicoccum triticum durum secale cereale hordeum vulgare and 3 common wheat cultivars a synthetic hexaploid wheat were observed.
We discovered that the awns are also able to propel the seeds on and into the ground. Glumes thick important in classification many varieties are awned awn extends from lemma photosynthesis ps occurs in awns awns contribute to grain yield in semiarid conditions but usually not in more humid conditions. During a period of increased humidity during the night the awns of the spikelet become erect and draw together and in the process push the grain into the soil. The dispersal unit of wild wheat bears two pronounced awns that balance the unit as it falls.